We are in industrial transport operations, often appear in the transfer cart of the left and right head swing problem; that is, we follow the process of linear form, and the transfer cart has uncontrolled left and right offset. First of all, we know that the trackless transfer cart is generally operated by remote control equipment; there are many reasons for this situation. Today, we will be based on a different situation together to analyse:
External Environmental Factors
Ground conditions: when the trackless transfer cart is on the road surface, there is unevenness, slopes, or obstacles, which may lead to lead to the vehicle travelling with an offset. Especially in the open operating environment, the road surface conditions are complex, such as oil, water or debris on the ground to increase the unilateral frictional resistance caused by the friction of different areas may resulting in a significant difference. This difference will cause the vehicle on both sides of that active wheel, the speed is not synchronous, and even trigger tyre skidding, ultimately leading to the direction of travel offset.

Trackless Transfer Cart Own Factors
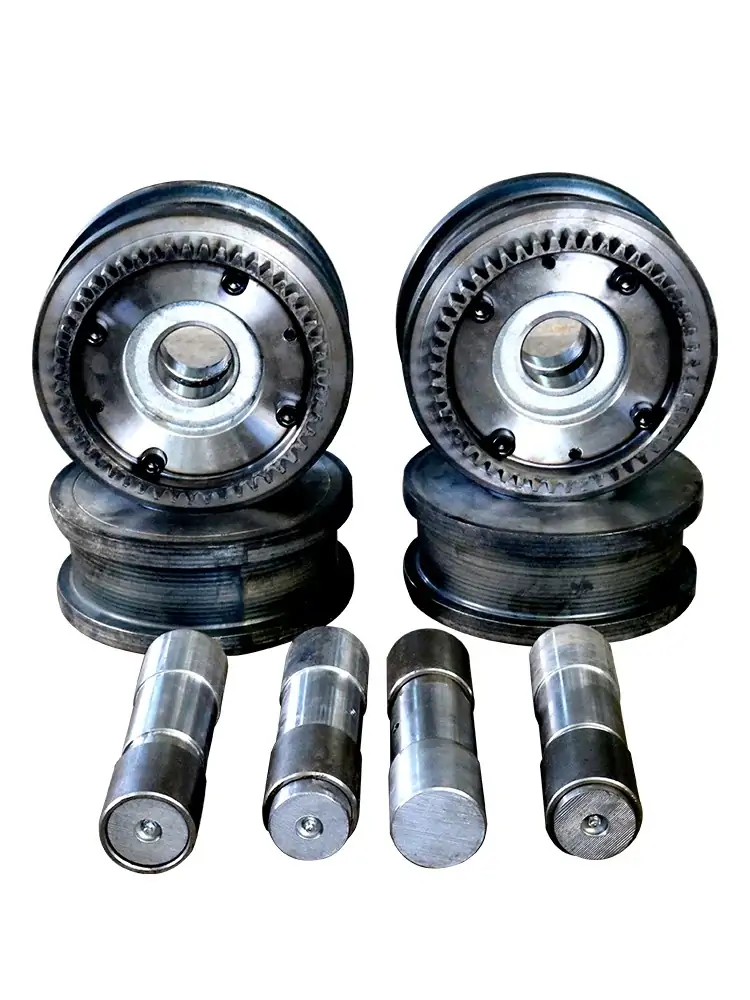
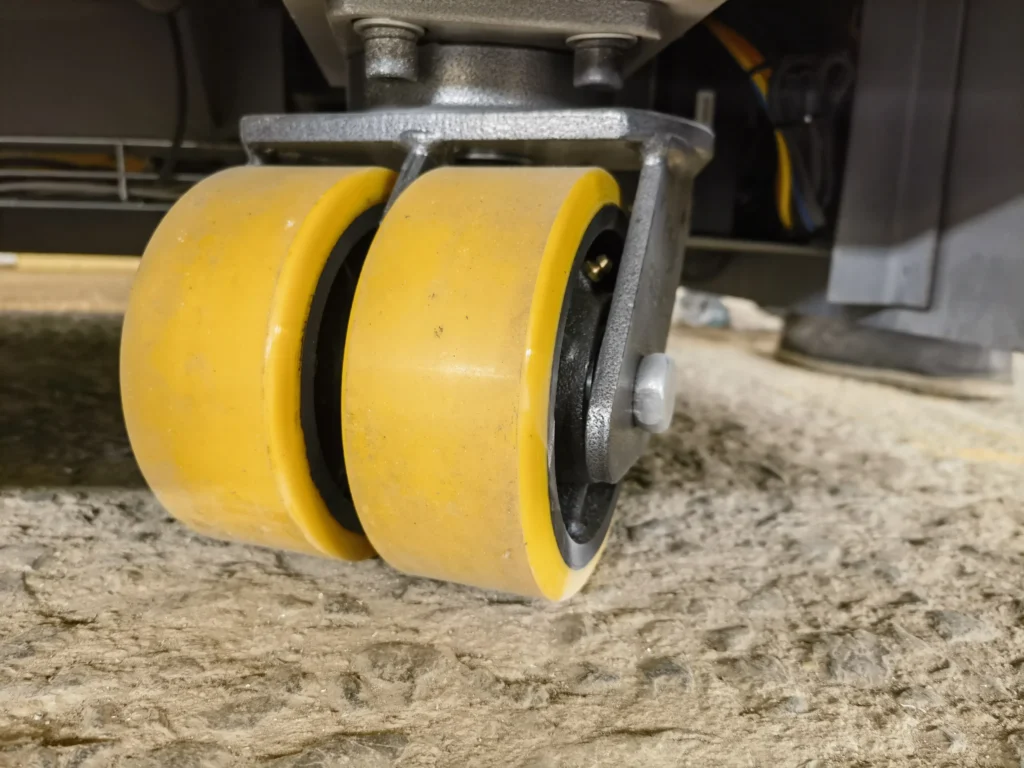
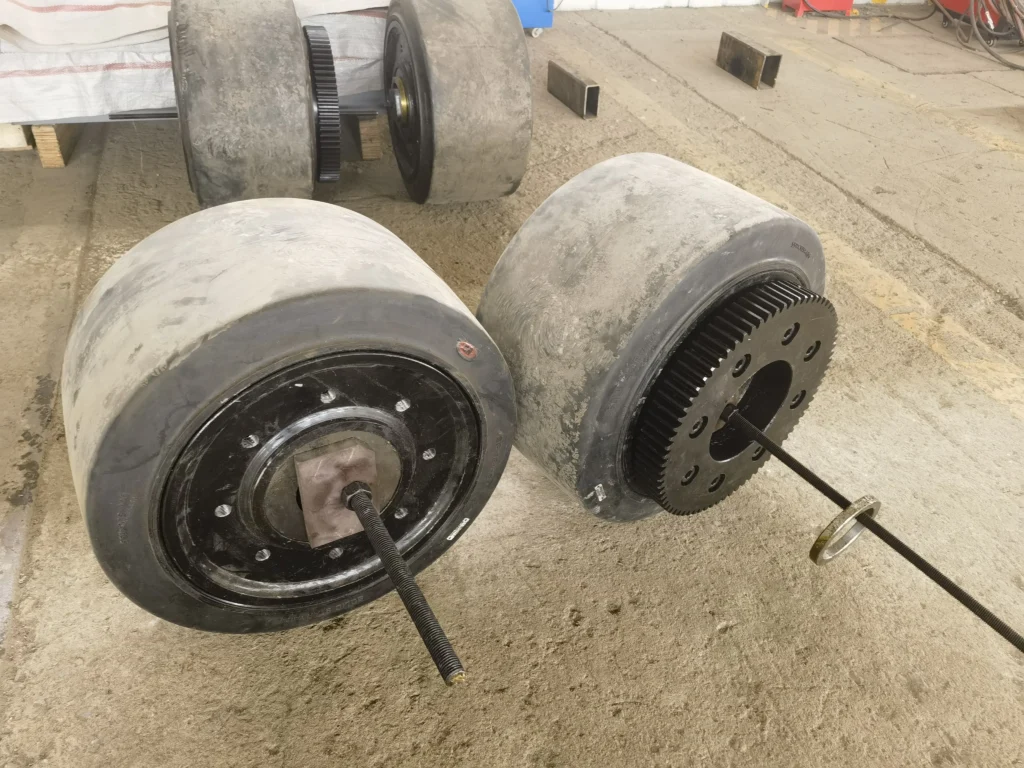
Wheel Problems: 1. Each wheel is made of slightly different materials, including uneven wear or inconsistent wheel diameters, which can lead to different speeds on both sides of the vehicle when it is travelling, thus resulting in an offset. 2. Errors in wheel mounting positions or damage to the bearings can also lead to unstable vehicle travel and offset. 3. Deformation of the wheels due to prolonged heavy loads or collisions can also lead to unstable vehicle travel and offset. 4. Inconsistent suspension spring/shock absorber stiffness, resulting in uneven wheel grounding pressure, may also lead to unstable vehicle driving and offset.
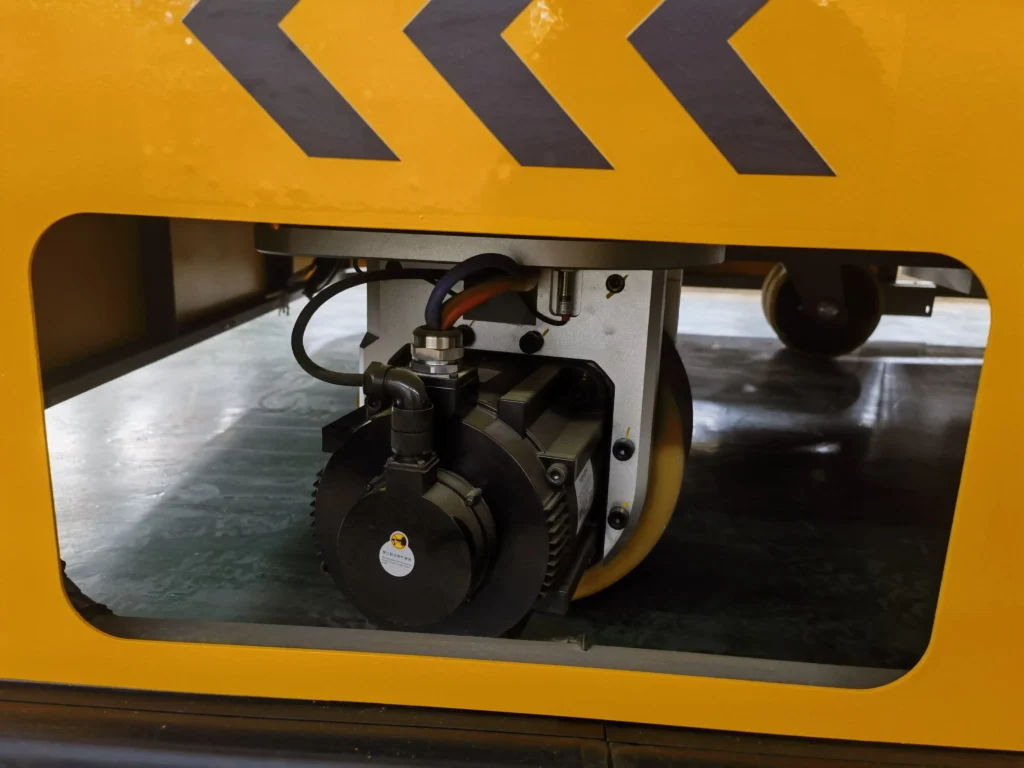
Drive system problems: 1. Inconsistent performance of the drive motor or mismatch of the drive ratio of the drive wheelset may result in different driving forces on both sides of the vehicle, which may cause offset. 2. Wear and tear or malfunction of the drive system (e.g., reducer, driveshafts, etc.) may also affect the performance of the vehicle’s straight-line driving. 3. Unsynchronised motor control signals (e.g., parameters not calibrated, encoder feedback abnormalities) may lead to uneven power distribution. It may also cause the vehicle to travel in a straight line 4. If the flat car relies on magnetic stripe, laser or visual navigation, dirty sensors, signal interference, or calibration error may cause deviation in path recognition.
Control System Failures: 1. Inaccurate instructions received by the controller or delays in executing the instructions may cause the vehicle’s direction of travel to be offset. 2. Failure or damage to sensors (e.g., position sensors, speed sensors, etc.) may also affect the control system’s ability to judge and execute, resulting in offset.
Operation and Maintenance Factors
Inadequate Operation: Failure of the operator to accurately control the direction and speed of the Trackless Transport Vehicle during operation may result in offsetting of the vehicle while travelling.
Inadequate maintenance: Regular maintenance and upkeep of the trackless transfer cart is an important measure to ensure its stable travelling. Insufficient maintenance, such as failure to timely replace worn parts, adjust the wheel position, etc., may lead to vehicle drift when driving.
In summary, the reasons for the deviation of trackless carriers when travelling in a straight line may involve the external environment, the vehicle itself, operation and maintenance and other aspects. In order to ensure the stable travelling of the trackless transfer cart, it is necessary to consider these factors comprehensively and pay attention to the use of remote control to correct the direction appropriately during the operation.

Trackless Transfer Cart Solutions:
Optimise the ground: Regularly clean the road surface of oil, water and debris, repair uneven areas, and lay anti-skid steel plates or wear-resistant coatings at easy-to-slip places to reduce the difference in friction from one side to the other.
Wheel and Drive Inspection: Monthly inspection of wheel diameter, bearing clearance and suspension stiffness to ensure even grounding pressure. Automatically adjust the motor speed according to the wear data. Replace tyres or adjust suspension if deformation or excessive wear is found.
Motor and navigation calibration: Calibrate the motor encoder quarterly to synchronise the speed of dual motors, and clean and calibrate the sensors regularly.
Standardised operation and maintenance: Operators need to be licensed. Check tyre pressure and sensor cleanliness daily; test motor balance weekly; change gearbox lubricant every six months. Record the offset data and analyse the high-frequency failure points, and replace the wearing parts in advance.
Conclusion:
Through the above analysis, we know the Reason for the automatic direction shift when the Trackless Transfer Cart travels in a straight line and the solution. If you have more questions about the transfer cart, you can contact us at any time. We are professional electric transfer cart manufacturers have rich experience in solving your handling problems. Looking forward to your contact.